In today’s social media savvy world, we are all familiar with various social media websites like Facebook, Twitter, etc. or e-commerce giants like Amazon & Flipkart or for that matter any website that stores user data. This data can be anything right from the customer name, age, address, card details, photographs, comments, reviews etc. So, simply put data is information that is stored on a computer system which can then be used by the application whenever needed. When it comes to data being transferred over the internet, it is stored on the website’s web server. From the server, it then is stored in a database. A database is an organised collection of data that can be accessed, managed and updated easily.
One of the most crucial decisions when developing an application is the choice of the database you would use to store data. And irrespective of whether you have sufficient technical knowledge or not, this decision can seem to be difficult. After all, this is a matter of not just storing data but also retrieving it and all in a short span of time! Especially given the fact that the consumer market is growing at a rapid pace with heaps of data – courtesy, Internet of Things, and all things social and connected. If you’re building a business app then you should anticipate such high-volumes of data and to cope with it, the choice of database is extremely important.
Take, for instance, Amazon, a popular e-commerce giant. As a customer, if you have shopped from Amazon you would have noticed two things. One, whatever or however long your query is in the search box, it takes a matter of few seconds for the results to be displayed (keep in mind, your internet connection is good and not poor. Secondly, if you’ve added certain items to your cart or are browsing them, you would notice the ‘Frequently bought together’ option. Now, imagine the customers Amazon has and the amount of data as well, to sort this in a matter of seconds is quite a task. But you’ve not experienced this have you? Well, the reason is, Amazon uses its own NoSQL database, DynamoDB that doesn’t store data in tables and hence, it is easier to locate it. That being said, we will cover how it does this in the latter part of the article.
Moving on, in this article, we aim to help you understand why choosing a NoSQL database would be beneficial to you in the longer run. However, before we move on to that, let us first understand the concept of a database, popular database models available today and the reason you should switch to a NoSQL model.
Types of Databases:
A database is a collection of data that can be easily accessed, managed, updated and deleted. There are several database types, however, databases can be broadly classified into the following four types:
- OODB or Object-Oriented Database
- RDB or Relational Database
- NoSQL (Not only SQL) and,
- NewSQL (a class of RDBMS)
For the sake of simplicity out of these 4, we will choose the two popular database models viz. Relational Database and NoSQL.
In a relational database, the data is stored in ‘Tables’ in the form of rows and columns. It uses the SQL (Structured Query Language) pronounced as ‘Sequel’ to perform data-related operations like creating a table, inserting & reading data to/from it, modifying & updating data, and deleting the data or the table. These operations are most commonly known as CRUD operations. The data is connected to each other in a fixed schema. Informally, relational databases are also known as SQL databases.
Overall, a database is like a central repository or container with all the data and logs. Whereas, the schema is a folder in the database which groups together all connected objects logically. In simple terms, your bedroom is a table, your entire home is the database and your entire floor plan is the schema.
Some of the commonly used relational databases are, MySQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, SQLite, etc.
Moving on to NoSQL databases. NoSQL is a non-relational database model that doesn’t store data in the form of a strict schema or table as opposed to relational databases (we’ll cover how it stores data in the latter part of the article). Thus, your data can be of any type and still it could be stored or retrieved easily.
Why should you switch to NoSQL
Although relational databases are being used for good plenty of years and have fulfilled the demands of business in the past, things are now changing. With the increasing presence of the internet and usage of social media, the amount of data being generated is quite high in volume than it was maybe even a few years ago.
According to Domo, a platform that has been highlighting data in terms of its volume, velocity and variety since 2013, has seen a steep rise in the percentage of internet population and the data being generated every single minute! In its 7th consecutive report, the internet has reached 56.1% of the total world’s population and now represents 4.3 billion people, this is a 9% increase from January 2018. And as far as the trend goes, there won’t be a negative curve in the graph for a long time. This increase can be attributed to increased access to social media, popular internet services like YouTube, Netflix, etc. and interconnected sensors – the building blocks of the Internet of Things.
Given this staggering increase of data, managing it can be quite a task and relational databases are not quite adept at processing this rapidly. This is due to the fact that the new data coming in does not always fit into the tight schema followed by a relational database. NoSQL database, on the other hand, can easily manage huge volumes of data and the operations performed over it.
For instance, if you have a website that is popular and say has at least 10,000 registered customers, and growing daily, each of these customers will follow their own life-cycle and processes. On the front end, they would be loading pages, similar items, adding products to cart etc. but on the backend, whenever an operation is performed, the data is retrieved from the database, the similar items are suggested taking into account the number of times a particular type of query was run, and so on and so forth.
If all these operations take time to run say maybe more than a few seconds or a minute (i.e retrieving/reading from the database, searching, finding and displaying) the user might abandon the cart and go somewhere else.
The reason for slow operations could either be slow website loading speed or a slow backend that processes your data. If you have a relational database, chances are there would be innumerable rows and columns, and finding the right match would take a long time. On the other hand, if you use a NoSQL database, this problem would be significantly less.
So is this a real-time example? It is, Amazon uses DynamoDB as mentioned initially, and Google uses BigTable, both an example of a NoSQL database.
To put it simply, here are the 4 reasons to switch to a NoSQL database:
- Highly scalable
- Able to handle large volumes of data – structures, and semi-structured
- Schema-less
- Quick iterations
Types of NoSQL Databases
Having seen the key advantages to switch to NoSQL databases, let us now move on to understanding the types of NoSQL database. Simply put, which type of database should you go for depending on the type of your business.
There are four types of NoSQL Databases viz. Key-value, Document, Column and Graph.
- Key-Value
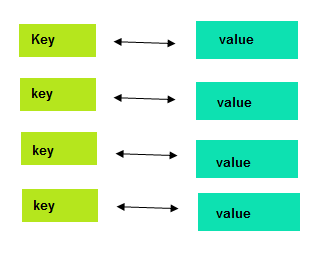
In the Key-value type of database, the data is stored in the form of key/value pairs in a hash table where the key is auto-generated & unique whereas, the value can be anything, for instance, a string, JSON, BLOB etc. This type of database is usually used as dictionaries or collections.
Where can you use it? This type of database is best for e-commerce or shopping cart based websites.
Example: Riak and Amazon’s DynamoDB are popular key-value NoSQL databases.
- Document
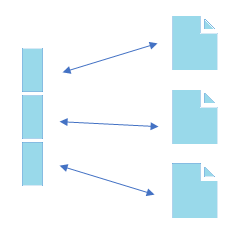
In Document-based NoSQL databases, the data is stored and retrieved as a key-value pair, however, here the value is stored in the form of JSON. BSON or XML type document. One of the key differences between a key-value database & document is that the latter embeds the attribute metadata that’s associated with the stored content, which then helps to query the data easily based on the content.
Where can you use it? This type of database is mostly used for Blogging or CMS platforms, e-commerce apps or real-time analytics, etc.
Examples: MongoDB and CouchBase are popular document-based NoSQL databases.
- Column
In Column-based databases, the data is written in the form of columns as opposed to the traditional row structure. Column-based databases use column orientation where each column is associated with a column key.
Where can you use it? Column-based databases are usually used to manage data warehouses, CRM, business intelligence, etc.
Examples: Google’s BigTable and HBase & Cassandra that were inspired by BigTable are some of the widely known Column databases. Cassandra was originally developed to solve the needs of Facebook’s Inbox search problem.
- Graph
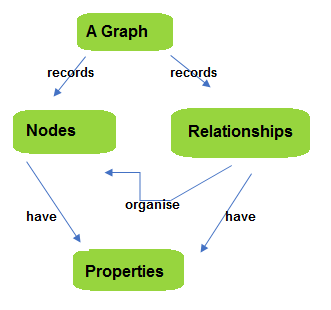
In a Graph-based database, the data is usually arranged in a flexible graphical representation as opposed to the strictures of tables or columns. Here, the database stores not only the object but also the relations amongst those objects.
For example, with reference to this diagram, the object/data is stored as a ‘node’ with the ‘relationship’ as edges. An edge establishes a relationship between nodes, and every node and edge has a unique identifier.
Where can you use it? Graph-based NoSQL databases are widely used for social networks, spatial data, logistics, etc.
Examples: Neo4J, Infinite Graph, OrientDB are some of the popular Graph-based databases.
How does it help your business:
We’ve seen the different types of NoSQL databases and various applications where to use them. If your business model falls into one of these and at the same time you deal with lots of real-time data, it would be a good decision to switch to a NoSQL database. At the same time, it is not necessary to have just one database in place, depending on the operations and the queries, you can have multiple databases.
For example, it can even be a combination of using MySQL (an RDBMS) for one particular operation because it is the best for that and use MongoDB for another.
In the end, what really matters is how much is your data and the best way you think is to handle it!
There is no ads to display, Please add some




